About UAE
General Information The United Arab Emirates is a constitutional federation of seven emirates; Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm al-Qaiwain, Ras al-Khaimah and Fujairah. The federation was formally established on 2 December 1971.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) occupies an area of 83,600 sq km along the south-eastern tip of the Arabian Peninsula. Qatar lies to the west, Saudi Arabia to the south and west, and Oman to the north and east. The capital and the largest city of the federation, Abu Dhabi, is located in the emirate of the same name.
Four-fifths of the UAE is desert, yet it is a country of contrasting landscapes, from awe-inspiring dunes to rich oases, precipitous rocky mountains to fertile plains.
The United Arab Emirates, one of the world's fastest growing tourist destinations, has all the right ingredients for an unforgettable holiday, sun, sand, sea, sports, unbeatable shopping, top-class hotels and restaurants, an intriguing traditional culture, and a safe and welcoming environment.
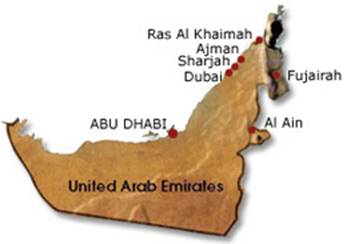
Map
Society & Culture | Head of State |
His Highness Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan |
| Land Area |
83,600 sq. km (square kilometers) |
| Population |
4,560,000 |
| CapitalCity |
Abu Dhabi |
| Religion |
Islam,Practice of all religious beliefs is allowed |
| Official Language |
Arabic |
| Time |
GMT + 4 hours |
| Currency |
UAE Dirham (UAE Dh) = 100 fils |
| International Dialing Code |
+971 |
| Weekend |
Friday and Saturday for government institutions |
The Seven Emirates
Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi is the largest of all seven emirates with an area of 67,340 square kilometers, equivalent to 86.7 per cent of the country’s total area, excluding the islands. It has a coastline extending for more than 400 kilometers and is divided for administrative purposes into three major regions. The first region encompasses the city of Abu Dhabi which is both the capital of the emirate and the federal capital.
Dubai
Dubai is the second largest Emirate in the UAE, a leading commercial centre and the Centre for hosting trade fairs and conferences in the Middle East. Dubai is the economic capital of the United Arab Emirates, has evolved considerably over the past years. Dubai lies between Abu Dhabi and Sharjah. It constitutes an important Emirate of money and business in the world, and point of tourist destinations for millions of tourists annually.
Sharjah
Sharjah is a city of learning and the arts, as confirmed by its 1998 UNESCO designation as the Cultural Capital of the Arab World. The city of Sharjah is home for more than 20 museums with splendid collections of artifacts and art as well as exhibits on science and natural history. Sharjah is the only emirate to have land on both the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Ajman
The Emirate of Ajman is situated on the coast of the Arabian Gulf, extending over a distance of 16 km, between the emirates of Umm al-Qaiwain and Sharjah. The area of the emirate is 259 square kilometers, equivalent to 0.3% of the country's total area, excluding the islands.
Umm al-Qaiwain
It is the second smallest emirate in terms of space. Umm al-Qaiwain is located between three emirates, which are Sharjah, Ajman and Ras Al Khaimah. Ajman and Sharjah lies at the south of the Emirate, and Ras Al Khaimah north. Also, Umm Al Qaiwain is smaller in terms of population. The Citizens depend on fishing and cultivating palm trees as source of income. But now Umm al-Qaiwain is developing and highlight features of the architectural renaissance.
Ras al-Khaimah
Ras Al Khaimah is the historical capital of the United Arab Emirates. Its area is 1700 square kilometres. Ras Al Khaimah is characterized by its green tree, which extends to cover a vast area of it. The city of Ras Al Khaimah which lies on the sea, has a long history stems from the flourished port and the special Pearl. The emirate is witnessing significant developments.
Fujairah
Fujairah holds a unique position in the UAE. It is the only emirate that lies on the eastern side of the UAE, along the Gulf of Oman, while all the six other emirates are along the Arabian Gulf. The area of the it is 1,300 square kilometers, which vary between mountains and plains and desert.Fujairah's main occupation in the past were fishing and agriculture.
Abu Dhabi Economy
Abu Dhabi Public-Policy Agenda
To be a competitive economy that would achieve sustainable economic development, raise the level of per capita income and lead to a competitive status with global economies. Abu Dhabi strategy is based on both the enhancement of the economic structure and the diversification of income sources through nurturing the non-oil sectors, strengthening the public-private partnership (PPP), encouraging the direct foreign investment (DFI), as well as through entering into joint ventures hinged upon comparative advantages. Any local economy managed by global standards seeks to apply the laws of the knowledge-based economy.
The most important element for such economy is the vision, which is composed of
- The availability of a secure society, and
- A dynamic open economy.
It should also be underpinned by the following pillars
- Premium education, healthcare and infrastructure assets.
- A large empowered private sector.
- The creation of a sustainable knowledge based economy.
- An optimal transparent regulatory environment.
- Complete international and domestic security.
- A continuation of strong and diverse international relationships.
- Emirate resource optimization.
- The maintenance of Abu Dhabi’s values, culture and heritage.
- A significant and ongoing contribution to the federation of the United Arab Emirates.
Abu Dhabi 2030 Strategy
The Strategy's most important objectives are:
- Adiversified macro-economy,
- An economy based on advanced technology,
- An economy built upon the best international practices,
- Export-oriented economy based on competitiveness,
- An economy based on skilled labor, and
- An economy based on quality and providing the best services in conformity with global standards.
The most important selected sectors are:
| The industrial sector |
The Energy sector |
| The knowledge-based sector |
The infrastructure sector |
| The financial sector |
Tourism |
Abu Dhabi in A Competitive World
Abu Dhabi is the number one city in the Arab world. Abu Dhabi seeks to integrate into the global market and to achieve prosperity for its citizens and residents. To make this a reality, it has taken up a scientific approach based on standards that would make it possible to measure its performance against that of other economies.
The International Institute for Management Development (IMD), based in Switzerland, and the Abu Dhabi Council for Economic Development prepared a report on Abu Dhabi Competitiveness in 2006, which aims to highlight the strengths and weaknesses in Abu Dhabi economy with the objective of creating an attractive business environment and of bringing about a competitive economy.
The number of countries covered by the comparison hit:
- 55 ones, and
- Abu Dhabi ranked 27 out of the 55 countries.
Abu Dhabi competitiveness is focused on the following standards:
| Macroeconomic Performance |
79 Standards |
| Government Performance |
72 Standards |
| Business Performance |
71 Standards |
| Infrastructure Performance |
101 Standards |
| Total |
323 Standards |
Global Competitiveness Index for the UAE:
We could not obtain the status of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi in the global competitiveness index, however, in 2006, the same index registered for the UAE a competitive indicator of 32 out of 128 countries and the same rank was also recorded in 2006. The UAE came first in terms of Arab countries' competitiveness.
Abu Dhabi in the Global Competitiveness List – Miscellaneous Comparisons
| Compared with |
Abu Dhabi's rank |
| Europe, the Middle East and Africa |
16 |
| Asia/Pacific |
9 |
| Americas |
4 |
| States with populations less than 20 million people |
18 |
| Average per capita GDP of more than 10 thousand dollars |
24 |
| Economies that depend on oil |
2 |
Essential Facts about Abu Dhabi in 2006
| |
Abu Dhabi |
Rank (out of 55) |
| Percentage of Real Growth in GDP |
11.5% |
1 |
| Average Per Capita GDP (One thousand Dollars) |
74.18 |
2 |
| Current account balance |
15.8% |
5 |
Abu Dhabi Economic Indicator 2007
| GDP at Current Prices |
$110Bn |
| GDP Annual Growth |
12% |
| Contribution of Non-oil Sectors to GDP |
$48 Bn |
| Annual Growth of Non-oil Sectors |
14% |
| Per Capita GDP |
$54000 |
| Contribution of Private Sector to GDP |
18% |
| Foreign Trade |
$84Bn |
| Annual Growth of Foreign Trade |
11% |
| Contribution of Foreign Trade to GDP |
77% |
Macro Climate Some Key Metrics 2007
| GDP |
$110 Bn |
One of the highest rates in the Middle East |
| GDP Growth |
12% |
Steadily increasing |
| Population |
2.0 m |
One of the wealthiest populations in the world |
| Per Capita GDP |
$54,000 |
One of the highest rates in the world |
| Inflation |
7.6% |
Expected to decrease |
| Trade Surplus as % of GDP |
49% |
Huge excessive liquidity |
| Trade as % of GDP |
77% |
“Open Economy” |
| Gross Fixed Capital Formation |
$17 Bn |
Steady remarkable increase |
| GFCF as % of GDP |
16% |
Expected to rise annually |
*GDP= Gross Domestic Product
*Bn= Billion, m=Million
Advantages for Investors
| Zero tax on profits |
5% customs duties |
| Industrial incentives |
Transfer of capital and profits |
| Advanced Telecom & IT |
International financial services |
| FTA with other countries |
Modern air and sea ports |
| Transparency |
Simplified procedures |
| Low labor-cost |
Real estate ownership (leasehold) |
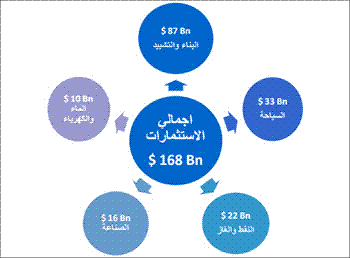
Future Investment Projects Up to 2010
Highest Moody’s “Credit Rating” in the Region
| UAE |
A1 |
| Kuwait |
A2 |
| Qatar |
A3 |
| Saudi |
Baaa1 |
| Egypt |
Ba1 |
| Jordan |
Ba2 |
| Lebanon |
B2 |
*Source: Moody's Q1/05
Tourism Information
Abu Dhabi, where luxury and style are infused with traditional values of hospitality and respect. Where sunny weather, tranquil beaches, lush oases, vibrant city life, and a mixture of culture and traditions come together to create a holiday experience like no other. Explore the emirate’s old souqs, sip a fragrant Arabic coffee, ride the dunes on an exhilarating desert safari, or dive into a dazzling marine life - there is something for everyone in Abu Dhabi.
Abu Dhabi is one of the most modern cities in the world. It is the center of government and business life in the UAE, headquarters of the emirates oil operating companies and embassies are based here. The architecture of its modern buildings and sky scrapers is the finest in the Middle East. Abu Dhabi's oil wealth has been wisely utilized to encourage a healthy trade and commerce atmosphere apart from oil industries too. The promotion of tourism and various tourism-related projects will elevate Abu Dhabi to a Singaporean status in the region. Large gardens and parks, green boulevards lining all the streets and roads, sophisticated high-rise buildings, state-of-the-art communication services and transport, the presence of all the international luxury hotel chains, rich shopping malls, cultural centers and events provide tourists a one-of-a-kind experience all the year round. Abu Dhabi’s second region, known as the Eastern Region, has as its capital Al Ain city.
Al Ain is a fertile oasis city located approximately 160 kilometers east of the Abu Dhabi capital. Its name ("the spring" in Arabic) derives from its originally plentiful supply of fresh water, which makes its way underground across most of the plain lying before the Omani mountains.
| Islands |
 |
Abu Dhabi emirate including nearly 200 islands are strewn along its coast. Visitors can use public transportation available to some of those islands. There is also renting boats for those who wish to do special trips to visit the islands.
Some of these islands: Lulu, Saadiyat, Al Futaisi , Horseshoe, Cut and Bahraini , Yas Island, Sir Bani Yas, Dalma. |
| Landmarks and Archaeological Sites |
 |
There are plenty of historical and contemporary sites for Abu Dhabi and Al-Ain visitors to explore in order to obtain an understanding of the local culture and heritage.
Some of these sites in Abu Dhabi: Al Maqtaa Fort, Heritage Village, Qasr Al Hosn , Women’s Handicraft Centre, Bateen Shipyard, Emirates Palace
Some of these sites in Al-Ain: Al Ain Palace Museum, Al Ain National Museum, and Hafit Mountain. |
| Mosques and Other Places of Worship |
 |
Abu Dhabi characterized by a large number of mosques which was designed mostly as engineering Islamic architecture. One of the rare architectural masterpiece is Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan mosque, one of the largest mosques in the world, where it is expands to more than 40 thousand prayer at one time. In Abu Dhabi there are available places of worship for different religions and sects |
| Music and Theatre |
 |
The Abu Dhabi Music and Arts Foundation organises regular concerts featuring the world’s top opera singers and classical music performers
Performing Arts Centre (Saadiyat Island)
Abu Dhabi’s own West End will come alive in 2011, once the 270-hectare cultural district in Saadiyat Island is completed |
| Cinemas |
 |
Visitors can catch the latest Hollywood, Bollywood and Arabic blockbusters at any of the emirate’s numerous cinemas.
In Abu Dhabi: there are eight major cinemas.
In Al-Ain: there are three cinemas.pleted |
| Shopping |
 |
There are over 10 shopping malls and centers in the capital. Two of Abu Dhabi’s biggest shopping malls are Marina Mall and Abu Dhabi Mall. Marina Mall is home for over 160 stores, and Abu Dhabi Mall, has over 220 stores. And other shopping malls and Traditional Souks
Al Ain also boasts several shopping venues, most notably Al Ain Mall. In addition to a number of brand name stores and 25 food outlets, Other shopping places in Al Ain include Al Jimi Mall and Al Ain City Centre. |
| Parks, Zoos and Natural Reserves |
 |
There are many parks in Abu Dhabi. On the other hand, Al Ain is known as the Garden City among its visitors. It has more than 70 parks equipped with leisure and entertainment facilities. Lush trees and landscape on the roadsides add to the beauty of the city.
Abu Dhabi: Sheikh Khalifa Park, Mushrif Garden, and other parks.
Al-Ain: Al-Ain Zoo, Mabzarah Al Khadra, Hili Fun City, Ayn-Al Fayda, and a large number of parks. |
| Sports |
 |
Abu Dhabi and Al Ain visitors enjoy watching and practice all kinds of sports such as water sports, equestrian, sand-skiing, golf, cricket, off-road driving, |